How to clone CentOS server to another one
How to clone CentOS server to another one
Step 1: Installing the Rsync Tool in CentOS
For cloning to be successful the rsync command-line tool needs to be present on both servers. This will be used for mirroring the source server to the destination server and syncing all the differences between the two systems. Thankfully, modern systems come with rsync already pre-installed.
To check the version of rsync installed run:
$ rsync --version
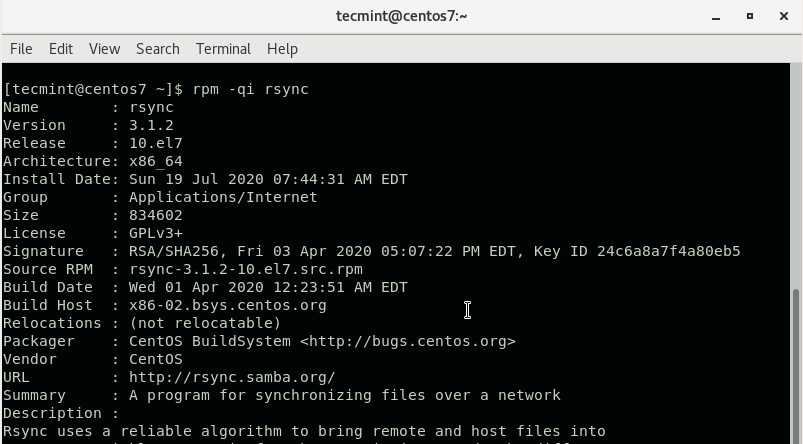
If you want to view additional information about rsync, execute the following rpm command:
$ rpm -qi rsync
If rsync is missing, run the following command to install it in RHEL / CentOS / Fedora systems.
$ sudo yum install rsync
Step 2: Configure the Source Server
There are directories and files that you may want to exclude from
cloning because they are either already available in the destination
server or are autogenerated. These include the /boot, /tmp and /dev directories.
Therefore, create an exclusion file /root/exclude-files.txt and add the following entries:
/boot /dev /tmp /sys /proc /backup /etc/fstab /etc/mtab /etc/mdadm.conf /etc/sysconfig/network*
Save and exit the configuration file.
Step 3: Clone the CentOS Server
With everything set, proceed and rsync your server to the remote or destination server using the command:
$ sudo rsync -vPa -e 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no' --exclude-from=/root/exclude-files.txt / REMOTE-IP:/
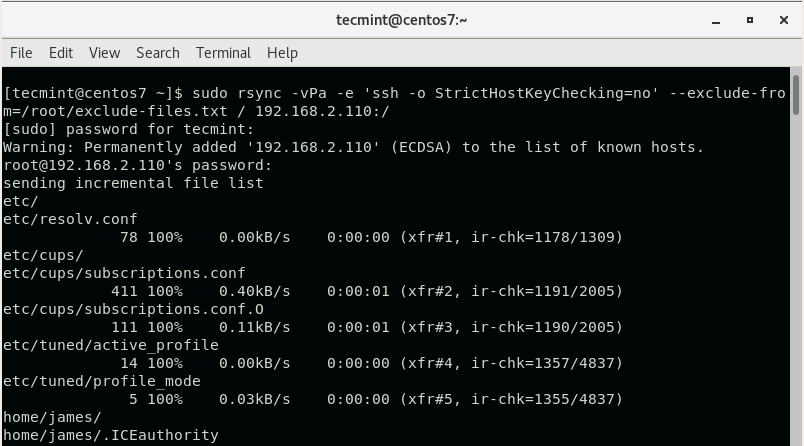
The command will rsync everything from the source server to the
destination server while excluding the files and directories you defined
earlier on. Be sure to replace the REMOTE-IP: option with your destination server’s IP address.
After the syncing is done, reboot the destination system to reload the changes and thereafter, boot into the server using the source server’s credentials. Feel free to decommission the old server since you now have a mirror copy of it.
found at: https://www.tecmint.com/clone-centos-server/
Comments
Post a Comment